Table of Contents
What is China Drug Master File?
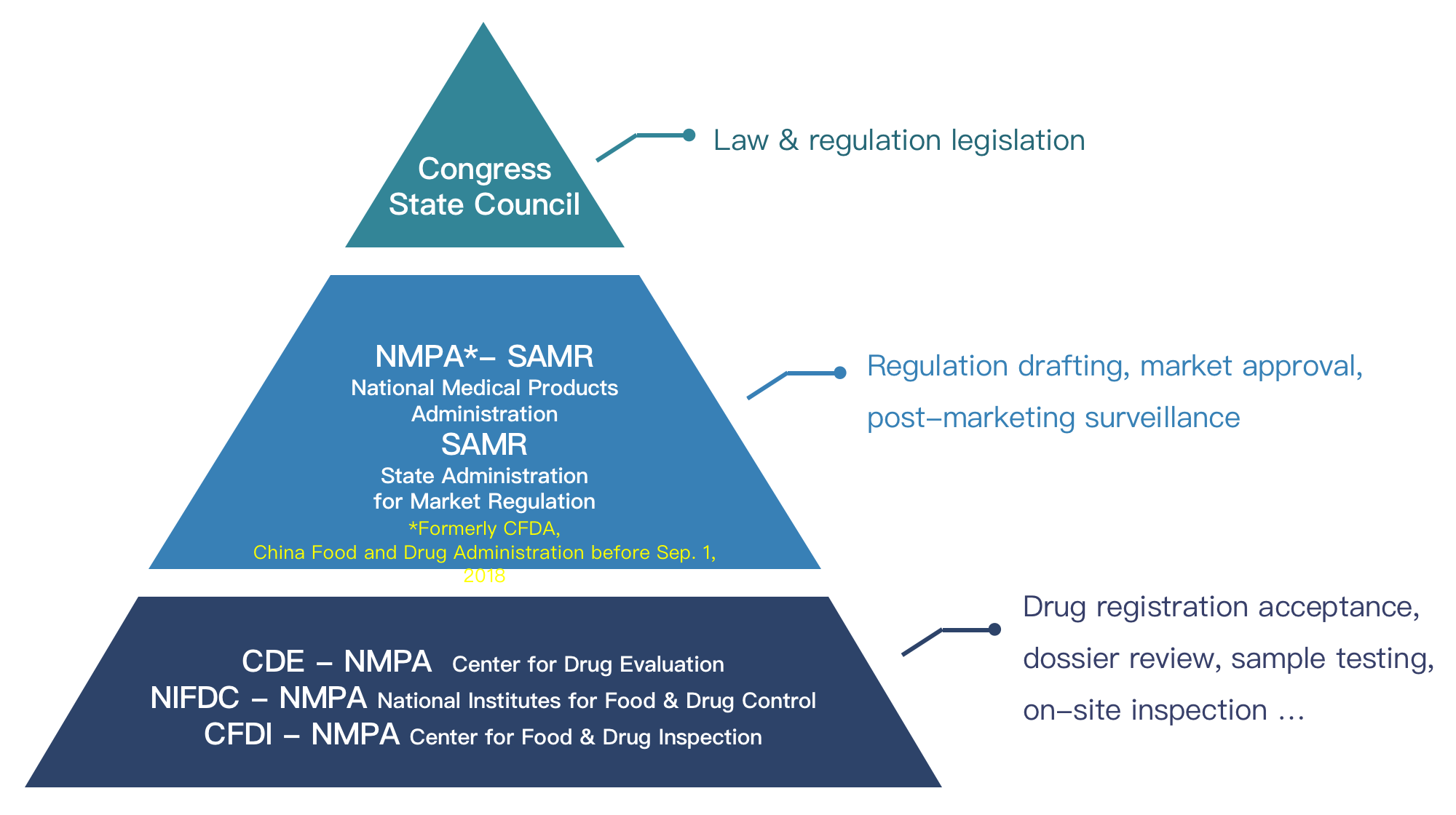
China’s NMPA for Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (APIs), Excipients and Packaging Materials introduced a NEW Drug Master File (DMF hereinafter) registration system since late 2017, reducing significantly more amount of cost and time for new medicines to land on Chinese market than before. It not only facilitates better intellectual property protection for manufacturers of APIs, excipients and packaging materials, but also streamlines the approval process for marketing of new medicines. It is notable that the new regulations stipulate that a local representative/agent should be appointed in China for overseas companies.Who is NMPA and CDE?
Definition
API (Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient) means the active ingredient which is contained in medicine. For example, an active ingredient to relieve pain is included in a painkiller. This is called API. A small amount of the active ingredient has an effect, so only a tiny part of the active ingredient is contained in medicine. You will find the name and amount of the active ingredient contained in the medicine on the package of OTC (over-the-counter) drugs.Essentials- Registration Process
a) DMF Pathway options
China has 3 pathways for AEP (abbreviated for “APIs, pharmaceutical excipients and pharmaceutical packaging materials”) approval.
The 1st pathway: Binding Review & Approval Similar to DMF in US and ASMF(Active Substance Master File) in EU, it is also the most common pathway under the new DMF policy. What this pathway in US, EU and China have in common is that the dossier binds with the finished drug product for technical review by authorities and allow valuable confidential IP or ‘know-how’ of the manufacturer of the active substance to be protected, while at the same time allowing the drug Marketing Authorization Holder (MAH) to take full responsibility for the drug product.
In this pathway, the AEP applicant prepares DMF dossier and submit application to CDE for completeness review. Afterwards, CDE will allocate a DMF filing number with a status of “I” for “Inactive”. This “I” status will also display on DMF filing database (also known as CDE database). At this stage, the applicant can export samples to China for the purpose of testing and study use. Subsequently, upon drug product registration (for example ANDA or NDA), CDE will refer to the inactive filing number and review the DMF dossier together with the drug dossier, and then activate the filing number shown as “A” for active if it passes the tecinical review. This “A” status will also display on CDE database.
The 2nd pathway: API Independent Review It is only for those APIs of any finished drug which had been marketed in China already (same APIs ever used in China). In this pathway, applicant will also obtain an inactive DMF filing number after completeness review. Afterwards, the application will directly proceed to CDE’s standalone technical review for subsequent activation.
The 3rd pathway: Part of Drug Dossier The third pathway is to include the AEP dossier as part of the drug product dossier. Therefore, for this pathway, as the AEP supplier, your data shall be shared with the drug applicant.
b) Registration Process
To submit a DMF, it is necessary to submit an application on CDE’s online platform. 1. DMF Dossier: Prepare DMF dossier for the products before submitting the applicantion to CDE. 2. Completeness checking: CDE conducts a format check on material completeness to identify if any required data is missing. 3. Application accepted: If complete, the application will be accepted. If incomplete, CDE will notify the applicant to submit the missing matierials within 30 wording days. 4. Inactive Filing No.: Upon acception of the applicaiton, an inactive DMF filing number will be issued, and the API filing adiministration fee should be paid. 5. sample testing and product specification review for APIs only : At the same time, CDE will also issue a notification letter of sample testing for APIs. The applicant should submit required documents and 3 batches of testing samples to National Institution for Food and Drug Control (NIFDC). NIFDC will assign a lab to conduct the sample testing, as well as to review the specification of the applied API. 6. Technical review: Before the application is approved, CDE conducts a technical review of the product in combination with the related finished drug–known as the Drug-related Associated Review & Approval process for binding review process, or a standalone techinical review for independent review process for API only. 7. Active Filing No.: Upon approval, the DMF filing number is activated. The product is authorized for marketing in China.
c) Checklist
Checklist for APIs: ✓ Application Form ✓ Administration Documents ✓ 2.3.S & 3.2.S (ICH M4 CTD) · Characterization · Process Validation · Impurity Research · Specification · CoAs · Container Closure System · Stability Study …
d) Timeline
A complete process of filing a DMF normally takes at least 6 months: 1. Preparing a DMF dossier could typically take 45-60 workdays. 2. After submission, dossier completeness will be checked by CDE in 5 workdays. 3. For any missing data, application acceptance could be extended to 30+ workdays. 4. After CDE completes reviewing the supplemented data, an inactive filing number will be issued normally within 1-2 weeks. 5. CDE’s technical review takes approximately 200 workdays (upon the acceptance of finished drug registration for binding reviews). Supplementary reviews could induce extra time, ususally 6-7 months including relevant material preparation. 6. Upon approval, the filing number will be activated in 20 workdays.
e) Costs
Administrative Fee: NMPA charges USD 50,000 for imported APIs for generic drugs and USD40,000 for imported APIs for new drugs.
Pitfalls & Tips
a)Pitfalls
To avoid a deficiency letter or even worse a rejection letter, it is necessary to pay attention to the pitfalls.
The most common pitfalls are mainly relating to the following parts: 1) manufacturing process, 2) quality specification and 3) impurity study 1. Around 35% of the DMF dossiers had issues with the data of manufacturing process, with problems occured in data incompleteness and process route. Data in completeness: The data provided is incomplete to meet CDE’s requirements or failed to fulfill the necessary details of the requirements. Therefore, it is crucial to identify these gaps as early as possible so they can be rectified in time, thus minimizing the risk of potential delay to market. Production process route: It does not comply with Chinese regulations that the starting materials selected is found too close to the finished product.
2. Around 25% of the dossiers had gaps in the quality specification. 3 notable examples: API content: Although there is no offcial regulatory requirement, normally, the API content limit in the specification should not exceed the tolerance range of 98%-102%, however in practice, sometimes it is easy to fall out of this range. Microbial limit: The microbial test in the specification fails to meet the required limit. Endotoxin test: In many cases, endotoxin test is easy to be neglected, resulting in the missing data for this field.
3. Around 15% had weaknesses relating to impurity study. For example, lacking of elemental, genotoxic impurities and impurity structural formula will induce undesirable outcomes from the CDE reviewers. Regarding the above pitfalls, ACCESTRA suggests you to prepare the specifications according to Chinese Pharmacopeia and related standards in a bid to minimize the risks as well as accelerate DMF filing process.
b)Tips
Top 4 tips for the abovementioned pitfalls:
1. to follow China’s regulatory updates. Given the fact that China’s drug policy is young and that significant reform and changes are happening frequently. It is very likely that new upcoming regulations replace the older ones, which could potentially impact your plan. Therefore, it is necessary to keep up to date and watch out for this space. 2. to have a strategic plan and to research for the quickest pathway options to China. It is very important to understand the pros and cons for different routes to market and adapt your market access strategy in China accordingly. 3. to “mind the gap” and “close the gap” . The importance of localization according to CDE’s requirements cannot be emphasized enough. Although China has joined ICH in 2017, there are still detailed differences in the technical requirements. Therefore, the gaps in the dossier shall be closed as much as possible to increase the chance of approval and accelerate the access to the market. 4. to appoint a local and capable agent. With different culture, language and requirements, it would be much easier to have a team of helpers on the ground to support you with activities in China.
References
1. Homepage of NMPA: http://english.nmpa.gov.cn 2. Homepage of CDE: http://english.nmpa.gov.cn/2019-07/19/c_389169.htm 3. Announcement for Adjusting Evaluation and Approval for APIs, Excipients and Packaging Materials (2017 No. 146): https://www.nmpa.gov.cn/yaopin/ypggtg/ypqtgg/20171130163301730.html