This is the second article in a series focusing on China Drug Master File (DMF) filing regulatory regulations and recent updates in the Chinese market.
Keywords: China DMF, API, Excipient, Packaging Material, Registration Strategy
Abstract
This article explores the detailed pathway options for China DMF registration, focusing on APIs, excipients, and packaging materials. It highlights the benefits and considerations of each pathway, providing DMF applicants with strategic insights to streamline their registration processes within China’s evolving regulatory framework. This content covered is essential for industry professionals seeking to understand and navigate the Chinese DMF registration requirements.
Pathway Options For Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs)
This article delves into three strategic pathway options and approaches that can be effectively employed to secure China DMF approval for your APIs:
- Binding Review and Approval Pathway: The API applicant submits a China DMF dossier to the CDE. If approved, an “Inactive” (I) China DMF filing number is assigned. During the drug product application, the CDE refers to the DMF number and changes the status to DMF “Active” (A) number upon approval.
- API Standalone Pathway: This independent standalone registration process allows the API to be reviewed and approved separately from the drug product, leading to an independent acquisition of the China DMF active number.
- Inclusion of API Dossier in Drug Product Dossier: In this approach, the API dossier is included with the drug registration documents, allowing for a streamlined review process while submitting additional information as needed.
Strategy 1: China DMF Binding Review and Approval Pathway
This strategy, the binding review and approval pathway, is the most common. The API applicant submits a DMF dossier to the Center for Drug Evaluation (CDE) for review. If approved, an “Inactive” (I) DMF filing number is assigned, allowing sample export to China for testing with NIFDC. During drug product registration (e.g., ANDA or NDA), the CDE reviews both the DMF and drug dossiers. Upon approval, the DMF status changes to “Active” (A) on the CDE DMF platform.
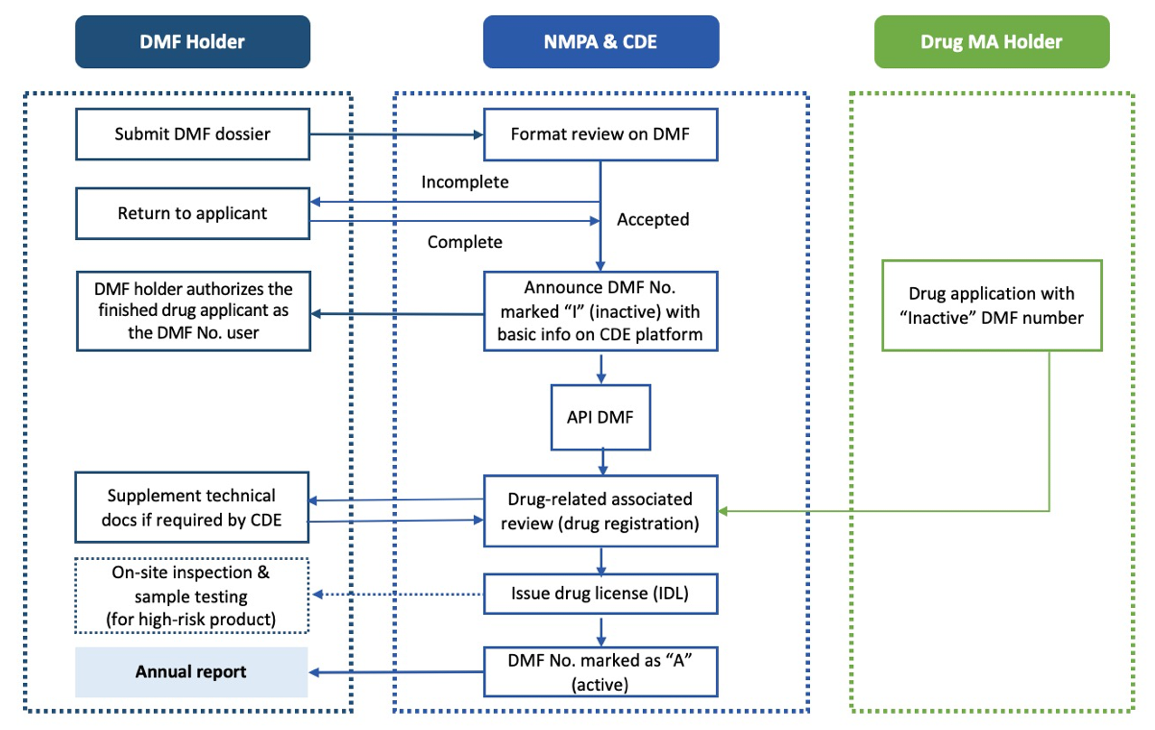
Binding review and approval pathway workflow (Figure 1)
Advantages
- Support from Drug Product Company: The API applicant may receive potential support from the associated drug product company, although such support is typically limited.
- Extended Preparation Time: If the associated drug product company needs more time to submit the Marketing Authorization Application (MAA), or if the API applicant is still seeking clients in China, this approach provides the API applicant with additional time to prepare supplementary documents. This extra time helps mitigate the impact of time constraints.
- Cost Savings: This strategy allows the API applicant to potentially save costs before the associated drug product company makes a final decision on the drug MAA. However, it is important to note that adherence to Center for Drug Evaluation (CDE) requirements may necessitate additional Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Controls (CMC) studies, requiring extra budget and time investment, which should be completed before the drug product MAA.
Considerations
- Dependency on Drug Product Approval: The approval status of the API is linked to the corresponding drug product registration. If the drug registration is disapproved, the API’s approval is also at risk.
- Pressure on Timeline and Outcome: Substantial pressure is exerted by the drug company regarding both the timeline and the final outcome of the API technical review. This is due to the direct impact of the API review result on the approval status of the drug registration.
- Potential Delays: Activation of the API DMF number may face delays due to an extended waiting period for the binding review with a drug company.
- Market Appeal: Drug companies prefer products with an active number when searching on the CDE platform. An active number is more likely to attract new clients, while an inactive number may hinder the company’s market appeal.
Strategy 2: China DMF API Standalone Pathway
The second strategic pathway is for China DMF API standalone review and approval, an independent registration process similar to the EU CEP certificate. Under this pathway, the applicant receives a China DMF inactive filing number after the completeness review. The application then moves to the CDE’s technical review, enabling the applicant to obtain a China DMF active number. This China DMF active number is crucial as it allows the applicant to commercialize and distribute the API to multiple clients.
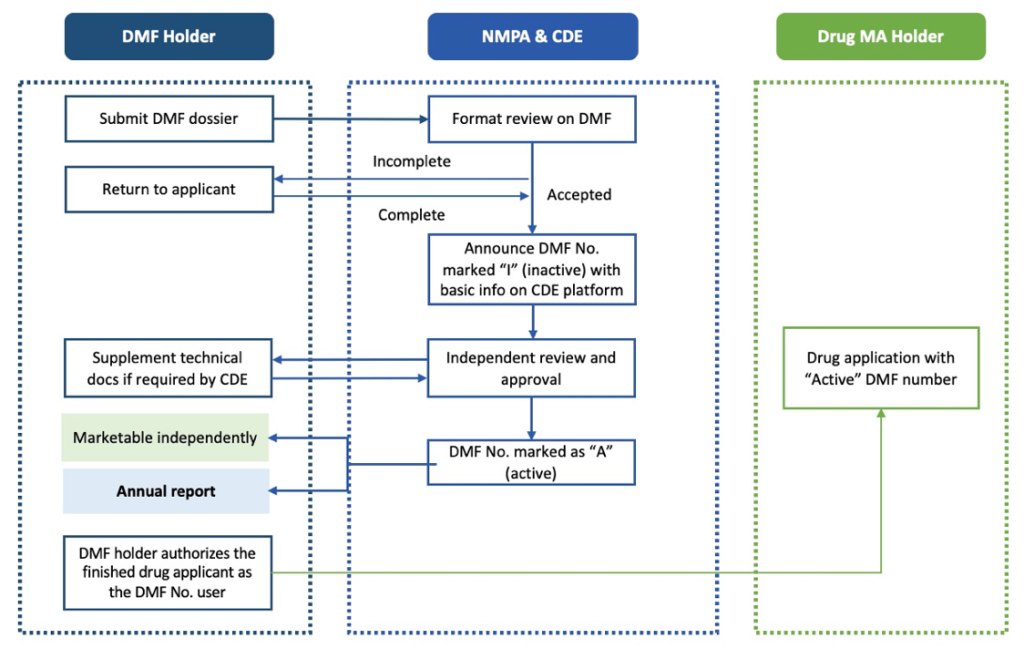
API standalone pathway workflow (Figure 2)
Advantages
- Independent Review Timeline: Standalone review offers an independent review timeline and results, free from the influence of the drug company.
- Accelerated Acquisition of China DMF Active Number: The standalone review process often speeds up the acquisition of a China DMF active number. This is due to the technical review that follows the initial format check closely, reducing unnecessary waiting time for the drug company to launch its MAA.
- Attracting New Clients: Securing a China DMF active number through a standalone review is appealing for attracting new clients since it reduces the risk of delays or issues with the APIs during the technical review by the CDE.
Considerations
- Meticulous Preparation Required: Successful implementation of standalone review requires meticulous preparation. All elements, including testing samples and supplementary documents, must be readily available within a compressed timeline.
Strategy 3: A Combination of Two Pathways
Step 1: Inclusion of API Dossier in Drug Product Dossier
In this approach, the API dossier is included with the drug documents during the drug registration process, but submitted independently by the API supplier. At this stage, API sample testing is not required. The need for testing will be determined by the CDE based on a risk assessment or any issues found in the documents.
During the technical review, if the CDE identifies any missing API documents, they will issue a deficiency letter to the drug company. The API supplier can then directly submit the required information to the CDE.
Step 2: Standalone Pathway Filing
The first step helps the API applicant understand the CDE’s specific requirements. With this knowledge, the API applicant can confidently submit a standalone application for a China DMF active number. At this stage, the applicant includes a complete set of documents, fully meeting the CDE’s expectations. This standalone pathway filing is crucial for obtaining the China DMF active number, which allows the API to be commercialized and distributed to multiple clients in China.
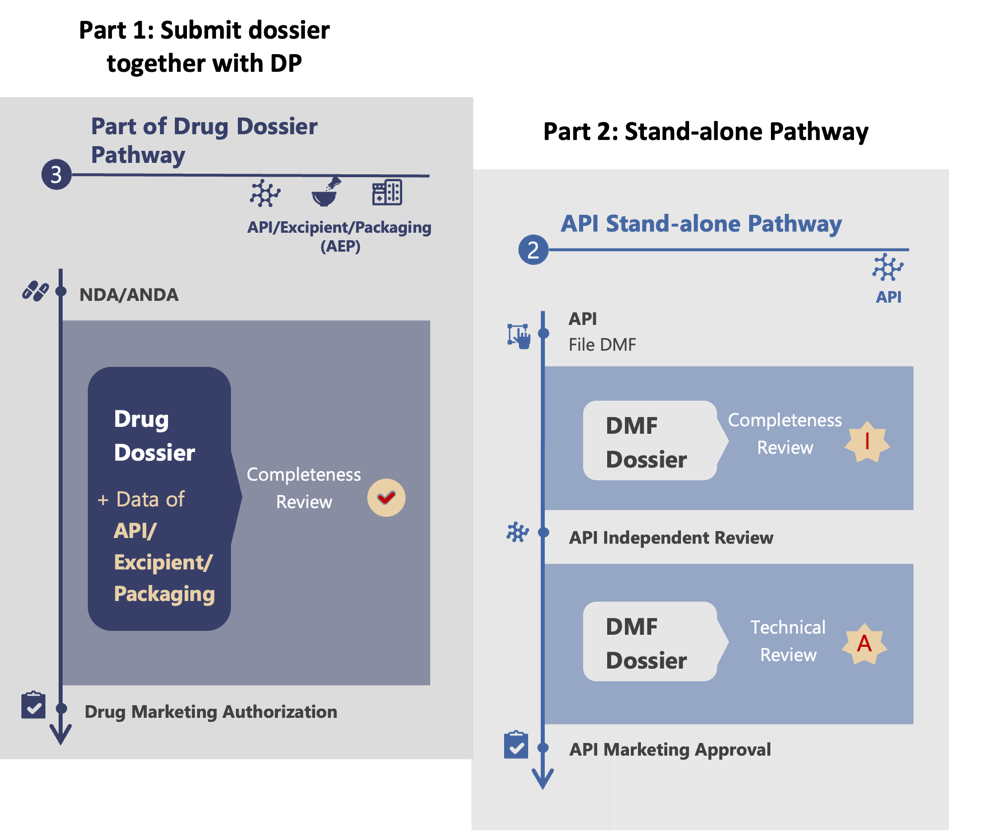
Part of drug product registration + standalone pathway workflow (Figure 3)
Advantages
- Time-Sensitive Projects: This approach is invaluable for time-sensitive projects where there isn’t enough time to compile a comprehensive dossier for China DMF filing, especially beneficial for an Investigational New Drug Application (IND) submission.
- Thorough Preparation: It facilitates thorough preparation for API document compliance, with a strong emphasis on specifications.
- Strategic Pre-Review: A pre-review by the CDE offers insights into potential areas of improvement, allowing for proactive preparation of supplementary documents and studies, better supporting the later DMF review process.
- Mitigates Testing Risks: This approach reduces the risk of triggering sample testing for registration (quality inspections) specifically for the API when submitting the API dossier alongside the drug documents.
Considerations
- Risk of Information Disclosure: There is a potential risk of confidential information disclosure with Inclusion of API Dossier in Drug Product Dossier. Since the API supplier lacks direct communication with the CDE, all information and requirements are initially relayed to the drug product company.
- Dual Submission Costs: Submitting the API dossier twice incurs an administration fee with each submission. This dual submission process adds complexity and demands additional resources, both in terms of time and costs.
Pathway Options For Excipient and Packaging Material Products
In the regulatory landscape for excipients and packaging materials in China, manufacturers have two primary pathway options:
- China DMF Binding Review and Approval Pathway: This pathway involves obtaining a DMF number.
- Part of Drug Registration: In this pathway, no DMF number is allocated.
For excipients and packaging materials, the most common and recommended option is to obtain a China Drug Master File (DMF) via the Binding Review and Approval Pathway.
Although including the excipients and packaging material dossier as part of the drug registration is an alternative pathway, this option also has critical drawbacks. It cannot guarantee the confidentiality of technical data, as all documents must be submitted through the drug company, risking exposure of confidential information. To safeguard this information, most manufacturers opt for the more secure route of applying for a China DMF number.
While options for excipient and packaging products may seem limited, a practical strategy can streamline the registration process. Documents can be updated any time before the binding review begins, offering more flexibility than API submissions. Manufacturers can address comprehensive gap closure or major defects before submission. Early decision-making allows for a customized approach aligned with project timelines.
Conclusion
As outlined, there are three distinct registration pathway options for API products and two for excipient and packaging products. Each pathway has its own set of advantages and considerations. It is crucial for applicants to carefully consider these factors when devising their strategies, ensuring they align with the unique circumstances of their projects.
The optimal pathway selection replies on a thorough evaluation of factors such as project timelines, available resources, confidentiality concerns, and the nature of the product itself. This customized approach maximizes the chances of regulatory success and expedites the approval process.
In conclusion, the diversity in registration pathway options for API, excipient, and packaging products requires strategic planning to avoid pitfalls and risks of delay. By carefully weighing advantages and considerations, applicants can craft tailored strategies that navigate the regulatory landscape in a timely and cost-effective way.
Author
This article was prepared by April Wang from Accestra Consulting, which provides China Regulatory Affairs Consulting and Drug Master Filing (China DMF) for APIs, Excipients, and Packaging Material.
Contact Us
For questions, please contact us by email: info@accestra.com or visit www.dmfchina.com for more information.
